Ask About Our Discreet Bed Bug Service
That’s right! When we show up to perform our bed bug pest control service, we are discreet about it. Whether it is at your home, business or restaurant, we show up in inconspicuous vehicles. Thus, keeping your pest control issue private, because having a vehicle with Pest Control, Bed Bugs or Roaches plastered all over it can be embarrassing and off putting.
Bed Bugs: Des Moines Iowa Pest Control Guide
Bed Bugs in Des Moines Iowa
According to Orkin’s Top 50 Bed Bug Cities List in 2021, Iowa is listed twice on as the most bed bug infested cities in the nation. Since humans are bed bugs’ primary food source, it makes sense for them to thrive in a highly populated cities like Des Moines, Iowa.
Iowans that live in Des Moines are constantly on the move, making it easy for bed bugs to travel around. Due to their small size, it is easy for them to “hitchhike” on your suitcases, clothing, furniture, purses, and clothing.
Bed bug season in the Des Moines area is year-round, meaning you could be dealing with these pests at any time. However, towards the end of the summer season, infestations increase as people begin to return from their summer vacations.


Facts About Bed Bugs Des Moines
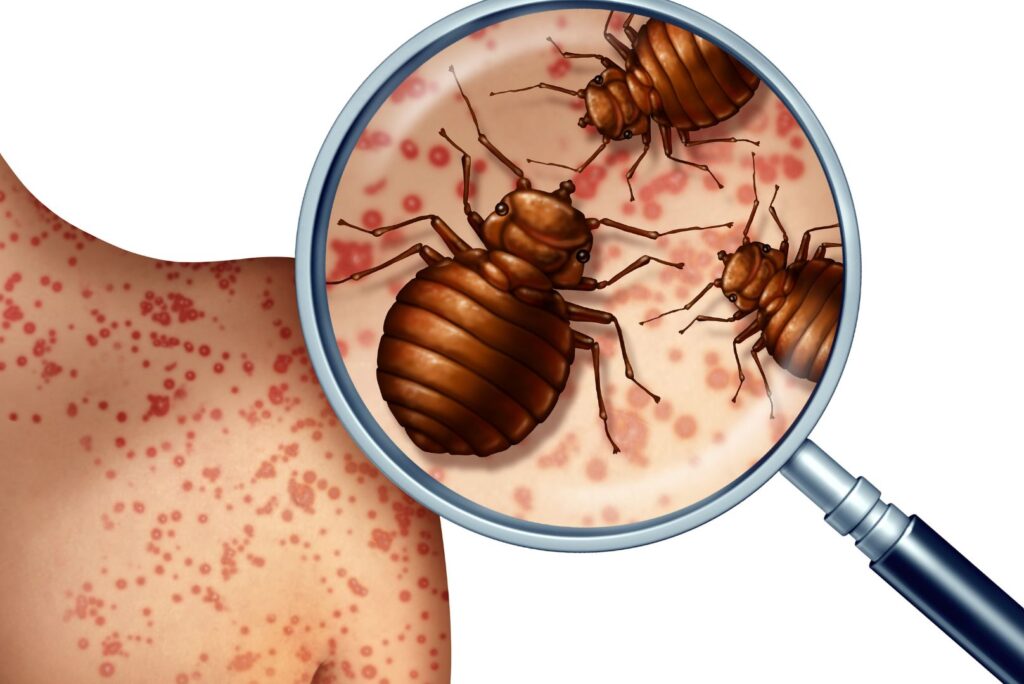
Bed bugs are tiny insects in the family Cimicidae. As ectoparasites, they feed on the blood of warm-blooded creatures, primarily humans.
Appearance
- Flat and oval-shaped
- Reddish-brown
- Usually 4-5 mm long (about the size of a flaxseed)
- Narrow head and thorax
- Wide abdomen
- Six legs
- Two antennae
- Small vestigial front wings (but can’t fly)
If a bed bug has recently fed, its body enlarges into a bloated, football shape and its color becomes a bright red shade. After it has digested the blood, its body flattens back into the usual oval shape..
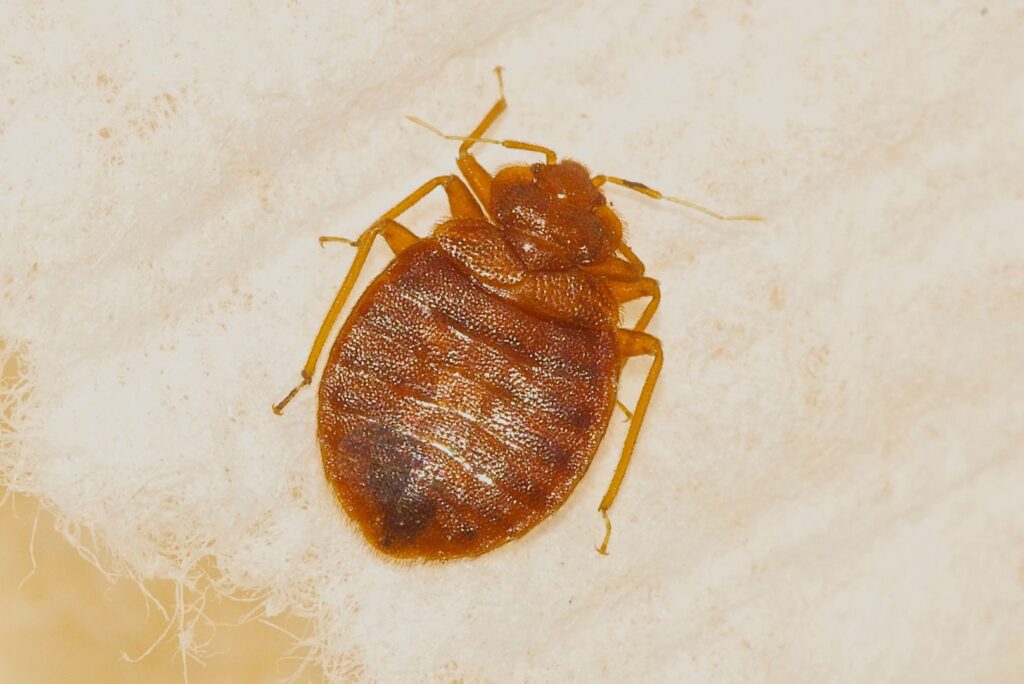

Species of Bed Bugs
There are only two species of bed bugs: the common bed bug, Cimex lectularius, and the tropical bed bug, Cimex hemipterus.
- Cimex lectularius is the most common species of bed bug in the U.S and parts of Europe. If you encounter bed bugs in your Des Moines home or apartment, Cimex lectularius is the usual suspect.
- Cimex hemipterus prefers the tropical habitats in Asia, Africa, and South America and is rarely seen in Des Moines.
- Other species of insects in the genus Cimex may appear similar to bed bugs but don’t typically feed on humans — for example, the common “bat bug” (Cimex adjunctus) feeds primarily on the blood of bats.
To the naked eye, these species look nearly identical. The only way to confirm which species of Cimex you have is to examine them under a microscope.
What Attracts Bed Bugs?
Contrary to popular belief, bed bugs are not attracted by dirt and grime. Instead, ; they actively seek out body heat, body odor, and the carbon dioxide that humans exhale.
- Bed bugs are sensitive to heat and temperature gradients, which helps lead them toward warm-blooded hosts to feed on.
- An increase in carbon dioxide (CO2) in the air due to breathing, especially during sleep, triggers foraging behavior in bed bugs. This causes them to leave their harborage areas and begin searching for the food source.
- Bed bugs are attracted to human body odor, using certain chemical compounds as signals to help orient them towards their prey.
- Residual body odor also attracts bed bugs to dirty laundry, which is why bed bugs find their way into luggage and suitcases before hitching a ride to new locations.
Bed Bugs on Pets
While bed bugs prefer feeding on human blood, they will occasionally also feed on other warm-blooded animals like dogs, cats, and rodents.
Some signs that a pet might have been bitten by bed bugs include vigorous scratching, skin rashes or inflammation, or dried blood on skin or fur.
Cleaning the bitten areas with antiseptic will aid the healing process and prevent infections.
Reproduction
Upon reaching adulthood, bed bugs will start to reproduce. A fertilized female adult bed bug can lay up to five eggs a day and up to 500 in her lifetime.
The average egg will take 6-10 days to hatch, and then another 5-6 weeks is required to reach adulthood.
Life Cycle
In order to fully understand the infestation level in your home, it’s a good idea to familiarize yourself with the bed bug life cycle.
If you’re able to identify bed bugs at different life stages, you can sometimes estimate the age of the infestation.
Bed bugs go through five developmental life stages in between the egg and adult stages. Each of these transitional stages, called nymphs or instars, requires a blood meal in order to develop to the next life stage. In order to grow larger, they have to shed their exoskeleton, leaving behind a translucent colored shell.
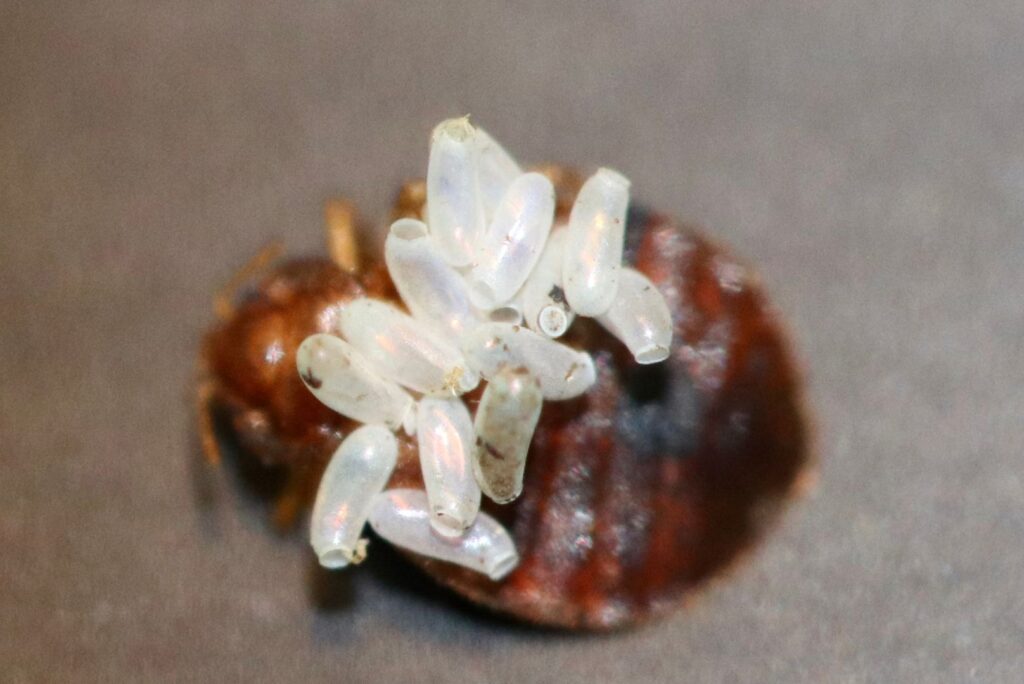

- Eggs
- Bed bug eggs resemble a grain of rice but smaller.
- Their shape resembles an elongated oval.
- They are pearly white or grey in color.
- The average length of a bed bug egg is approximately 1 mm.
- Bed bug eggs that are more than five days old have a small dark spot resembling an eye.
- At the end of the egg is a hinged cap, which opens up to allow a newly hatched bed bug to come out.
- Nymphs/Instars
- Bed bug nymphs can start feeding as soon as they hatch.
- Bed bug nymphs are translucent with yellow brown tint and around 1.5 mm in length.
- Once they feed, the nymph they will molt and then move onto the next stage
- In the fifth instar stage, bed bug nymphs become less translucent and grow to around 4.5 mm in length.
- Adults
- Bed bug nymphs that reach the final stage of maturity are considered adults.
- The average adult bed bug is between 5-7 mm long.
- Before they feed, adult bed bugs are brown, flat, and oval-shaped
- After they feed, they temporarily take on a darker, reddish-brown hue and will balloon in size into a football shape
- Under ideal conditions, with normal room temperature and an adequate supply of blood, adult bed bugs can usually live up to 10 months.
Common Signs of Bed Bugs
If you wake up with bites on your body, or have a neighbor or family member dealing with a bed bug infestation, you may want to keep an eye out for these common signs of a budding bed bug infestation:.
- Unusual Bedroom Odors — the smell of bed bug pheromones is musty and slightly sweet, sometimes compared to the smell of raspberries, almonds, or cilantro. Large amounts of bed bug feces, which contains dried blood, has an unpleasant rusty smell.
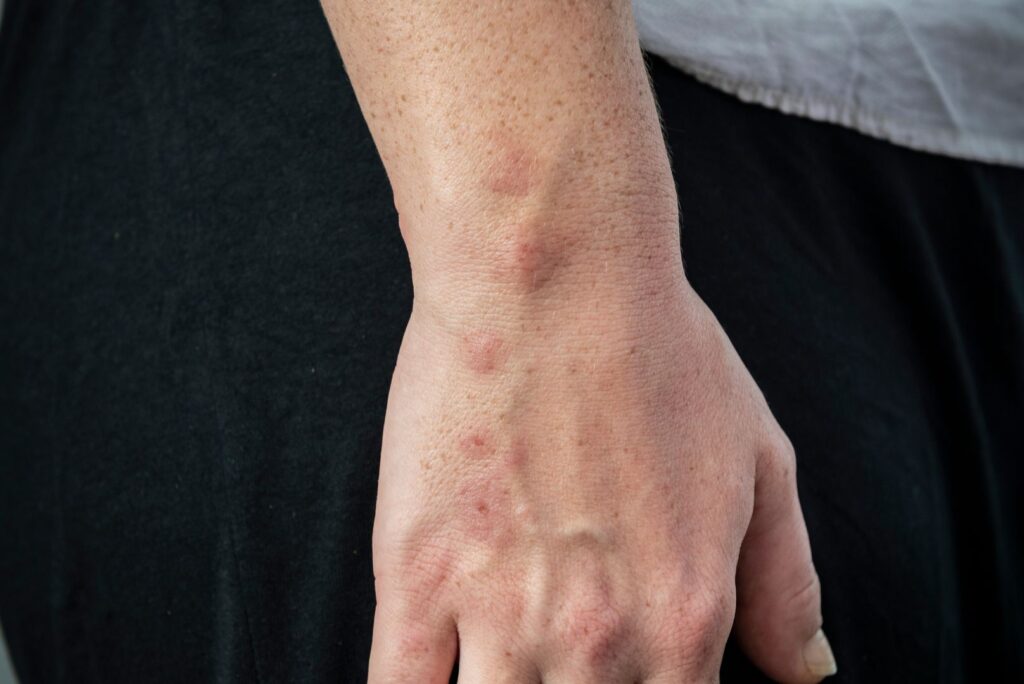
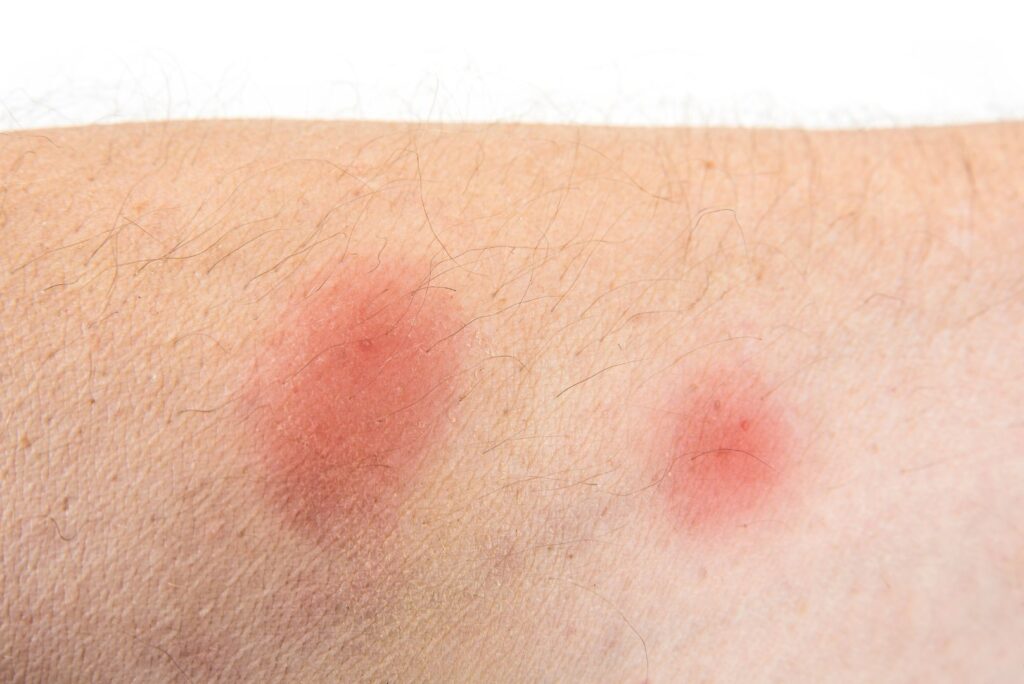
- Nighttime Bites — the most common presentation of bed bug bites are itchy red bumps that appear in small clusters on areas of the body exposed during sleep.
- Bloodstains on Sheets — tiny rust-colored blood stains may be left behind on sheets, pillows, and clothing after bed bugs finish feeding.
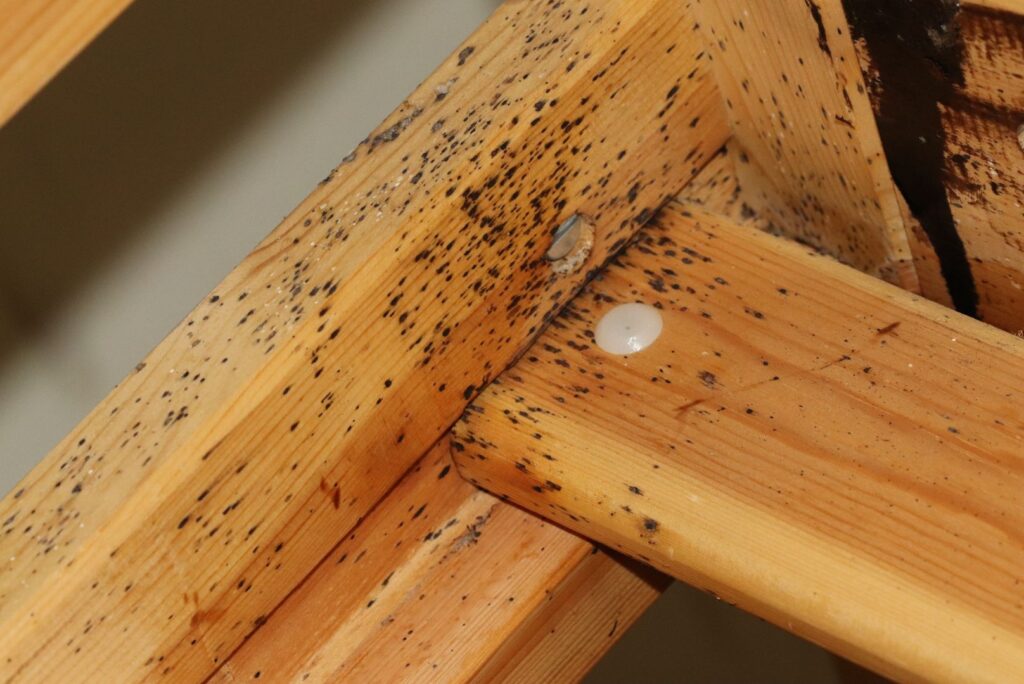
- Fecal Marks — bed bug droppings appear as small, dark brown or black dots about the size of a pen tip, and will smear on fabric when wiped with a moist towel.
- Bed Bug Eggs — pearly white, pinhead-sized ovals that are around 1 mm in length and resemble tiny rice grains. Usually found loosely stuck to surfaces where bed bugs hide.
- Shell Casings and Shed Skins — translucent, yellowish-brown exoskeletons shaped like juvenile bed bugs left behind after molting.
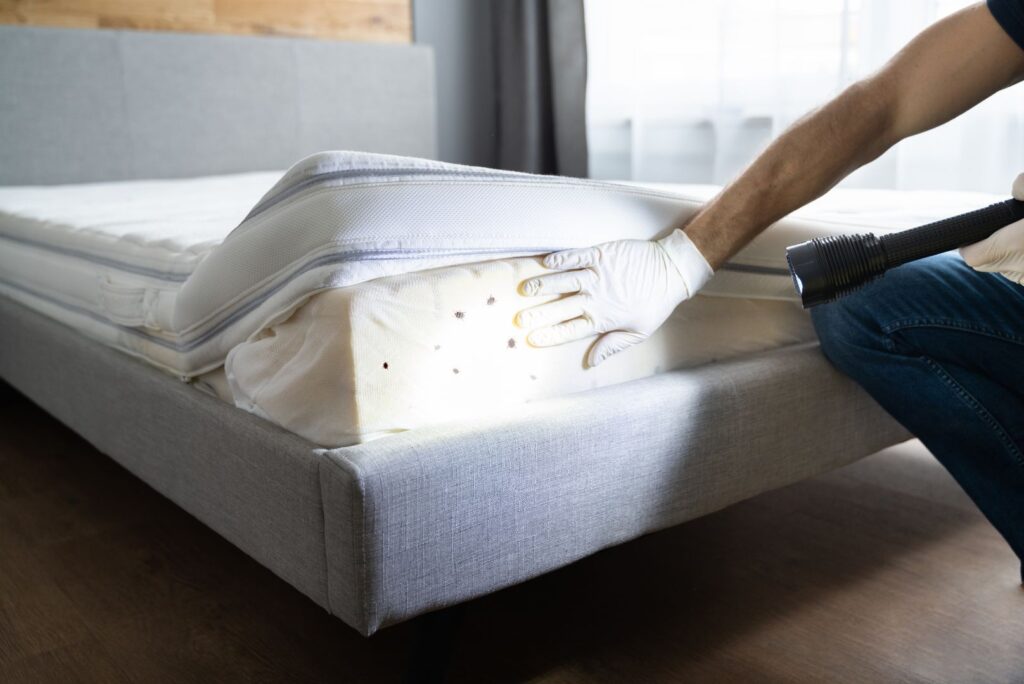
- Live Bed Bugs — flat, reddish-brown insects resembling flaxseeds that like to hide inside small, dark crevices such as the seams of a mattress or cracks within furniture.


Bed Bug Bites
Finding mysterious bite marks that seem to appear during the night is the most common way that people discover they have bed bugs.
Not everyone will react to bug bites in the same way. Some people might not have any reaction at all while others will find little red bumps or markings the next morning.
Itching and skin irritation in response to proteins within bed bug saliva is a relatively common symptom. Some people may also exhibit symptoms of a more serious allergic reaction, such as fever, flu-like symptoms, and an irregular heartbeat.
Bed Bug Feeding Behavior
Bed bugs normally come out and feed at night while you sleep. They typically feed every five to ten days, and each meal takes an average of 3-15 minutes.
When bed bugs bite, they pierce the skin with two hollow tubes — one injects saliva while the other extracts blood. Bed bug saliva includes certain compounds that act as an anesthetic and a mild anticoagulant so you won’t notice when you’ve been bitten.
If you happen to move in your sleep or if a bed bug is unable to feed in a certain spot, they may shift around and bite at a different spot until they’re full. This sometimes results in a zig-zag or line pattern of bites on your skin, referred to as the “breakfast, lunch, and dinner” pattern.
How to Tell if You Have Bed Bug Bites
There are a few common reactions to bug bites that might help indicate if bed bugs are the culprit. However, not everyone will react the same way, so some people may experience these reactions but not others.
- Raised little bumps
- Large welts or areas of redness
- Mild to moderate itchiness
- Small clusters or rows of bites
- Bites on parts of the body exposed during sleep, such as arms, legs, hands, and face.
Where to Find Bed Bugs
Once bed bugs have invaded your home, they can find a variety of different places to hide in.
In order to have convenient access to their food source, sleeping humans, bed bugs prefer to hide in mattresses and other furniture items around your bed. During the day, they are likely to seek refuge inside small crevices and seams on furniture like bed frames, headboards, baseboards, and nightstands.
From our experience as bed bug inspectors and exterminators, the most common bed bug hiding places include:
- Mattress seams and boxsprings
- Pillows and pillowcases
- Headboards, footboards, and bed frames
- Items and storage boxes underneath beds
- Corners and screw holes of dressers and nightstands
- Desk drawers and bookshelves
- Behind wall hangings and picture frames
- Cracks along baseboards and moldings
- Curtains and window frames
- Pet beds and children’s toys
- Electrical outlets
If you suspect that you might have bed bugs in your home, here’s a helpful guide about where to look for them: How to Check for Bed Bugs: Performing a Self-Inspection of Your Home or Apartment
How to Prevent Bed Bugs
There’s no way to 100% guarantee that bed bugs will stay out of your home, since there’s always the possibility of new bed bugs being brought inside from bags and clothing.
There are, however, certain habits and best practices that may help protect you from a bed bug infestation.
How Do Bed Bugs Spread?
Bed bugs are small, flightless insects that can’t crawl more than 20-40 feet a day. So why does it seem so easy for bed bug infestations to spread?
Research has established two primary ways by which bed bugs can find their way into your home: passive dispersal and active dispersal.
⦿ Passive dispersal
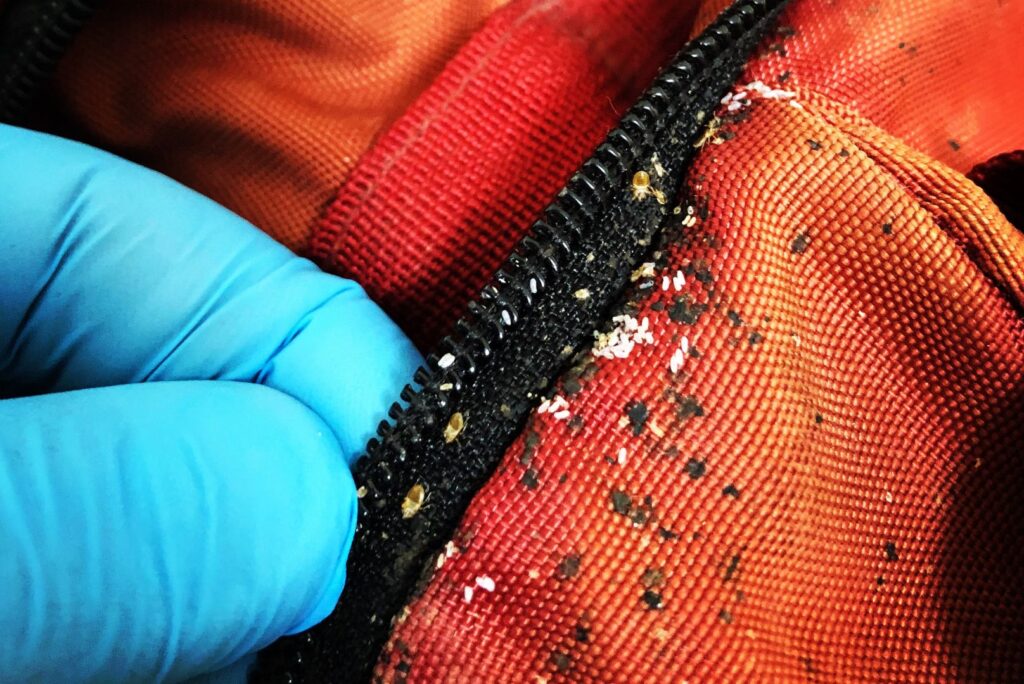
Passive dispersal happens when humans inadvertently carry bed bugs to new locations in our clothes, luggage, bags, furniture, and other items.
That’s why the spread of bed bugs has been linked to travel activity, especially overnight travel and hotel stays. Some examples of passive dispersal include:
- Bed bugs hiding inside folds and pockets of clothing
- Bed bugs in a hotel room finding their way into luggage or dirty laundry
- Bed bugs latching onto seams or zippers of bags and backpacks
- Bed bug-infested furniture discarded on a sidewalk and then picked up by someone else.
- Bed bug-infested laundry placed on shared surfaces at a laundromat
⦿ Active dispersal
Active dispersal refers to bed bugs crawling around on their own, wandering from one home to another.
This usually happens with pregnant females looking for new places to lay eggs. Bed bugs can’t travel far, so the range of active dispersal is typically limited to neighboring apartments in the same building.
Bed Bug Prevention Tips
- Store clothes in sealed bags when traveling
- Wash clothing in hot water when returning home from vacation
- Inspect luggage and bags before bringing them inside
- Wash bed sheets and pillow cases frequently
- Vacuum floors and reduce clutter
- Use a mattress encasement to cover your mattress and box spring
- Inspect any new or used furniture before bringing it home
Bed Bug Solutions
Bed bugs spread quickly and can hide in many hard-to-reach places, which makes it difficult to exterminate them completely. If you don’t get rid of every single bed bug and viable egg, there’s a good chance that the infestation will reoccur.
Bed Bug Solutions
Bed bugs spread quickly and can hide in many hard-to-reach places, which makes it difficult to exterminate them completely. If you don’t get rid of every single bed bug and viable egg, there’s a good chance that the infestation will reoccur.
How Do Bed Bugs Spread?
Bed bugs are small, flightless insects that can’t crawl more than 20-40 feet a day. So why does it seem so easy for bed bug infestations to spread?
Research has established two primary ways by which bed bugs can find their way into your home: passive dispersal and active dispersal.
⦿ Passive dispersal
Passive dispersal happens when humans inadvertently carry bed bugs to new locations in our clothes, luggage, bags, furniture, and other items.
That’s why the spread of bed bugs has been linked to travel activity, especially overnight travel and hotel stays. Some examples of passive dispersal include:
- Bed bugs hiding inside folds and pockets of clothing
- Bed bugs in a hotel room finding their way into luggage or dirty laundry
- Bed bugs latching onto seams or zippers of bags and backpacks
- Bed bug-infested furniture discarded on a sidewalk and then picked up by someone else.
- Bed bug-infested laundry placed on shared surfaces at a laundromat

⦿ Active dispersal
Active dispersal refers to bed bugs crawling around on their own, wandering from one home to another.
This usually happens with pregnant females looking for new places to lay eggs. Bed bugs can’t travel far, so the range of active dispersal is typically limited to neighboring apartments in the same building.
Bed Bug Prevention Tips
- Store clothes in sealed bags when traveling
- Wash clothing in hot water when returning home from vacation
- Inspect luggage and bags before bringing them inside
- Wash bed sheets and pillow cases frequently
- Vacuum floors and reduce clutter
- Use a mattress encasement to cover your mattress and box spring
- Inspect any new or used furniture before bringing it home
Bed Bug Solutions
Bed bugs spread quickly and can hide in many hard-to-reach places, which makes it difficult to exterminate them completely. If you don’t get rid of every single bed bug and viable egg, there’s a good chance that the infestation will reoccur.
For Finding & Identifying Bed Bugs
⦿ Traps and Monitors
If you are still unsure if you’re dealing with bed bugs, using special bed bug traps can help. Traps are used to monitor and confirm if you have a bug problem, not to eliminate it.
There are several types of bed bug traps on the market, but we recommend the ClimbUp Interceptor, which is designed to catch any bed bugs trying to climb up or down your bed.
These plastic dish-like devices have two walls that are rough on the outside and smooth on the inside, so that bed bugs can climb in but not out. When placed beneath the legs of your bed, they act like a moat to trap and capture bed bugs.
If you can’t find bed bug interceptors near you, homemade tape traps are another option. Have the sticky side of the tape facing up and lay the pieces around your mattress or bed frame before you go to sleep. In the morning, check the traps to see if anything was caught.
⦿ Bed Bug Sniffing Dogs
Because bed bugs are so small and good at hiding, it’s difficult to spot them relying on your eyes alone. Even if you manage to find some,there might be more bed bugs hiding in other locations that you’re not aware of.
Luckily, dogs can be specially trained to help detect bed bugs by sniffing out their scent.
Scent detection canines can find bed bugs and viable eggs with a much higher accuracy rate compared to a traditional visual inspection performed by a human. According to this 2008 study at the University of Florida, trained dogs were 98% accurate in locating live bedbugs.
Canine bed bug inspections are best suited for detecting early-stage infestations since a dog’s nose is so sharp that they can pick up traces of individual bed bugs. Being able to catch onto an infestation early — and know exactly where the bed bugs are hiding — drastically improves your chances of successfully exterminating them.
For Getting Rid of Bed Bugs Yourself
Sometimes an early bed bug infestation can be handled by yourself.
However, be aware that there is a risk involved — if you’re not successful, you’re instead giving the bed bugs time to breed and multiply. By the time you call in a professional bed bug exterminator, the costs of treating the infestation might be significantly higher than if you called them in the beginning.
If you have a bed bug infestation in your home and want to try tackling them yourself, here are some recommended methods to save your belongings and kill the bed bugs.
⦿ Washing and Drying on High Heat
In order to kill any bed bugs infesting your clothes and sheets, wash and dry them on the highest heat settings. A minimum temperature of 118°F (48°C) for a combined 90 minutes should be used to kill bed bugs with a 100% mortality rate.
Prior to washing, place infested items in sealed trash bags, and dispose of the trash bags immediately after the clothes and sheets have been placed in the wash.
After your items have been cleaned, place them in clean trash bags to prevent them from becoming re-infested.
⦿ Vacuuming
Use a high-powered vacuum with a crevice tool attachment to suck up any bed bugs that you find. Start around your bed and check bedsheets, mattress seams, and around the bed frame. Slowly expand your search outwards through the rest of your home.
After you’re done vacuuming all of the nooks and crannies where bed bugs might be hiding, spray the area down with an isopropyl alcohol solution with a concentration of 80% or stronger.
Lastly, empty out your vacuum into sealed plastic bags and sanitize the vacuum chamber with the alcohol solution.
⦿ Steaming
Using steam to treat a bed bug infestation is another effective, non-chemical option. In order to kill bed bugs and bed bug eggs with heat, the temperatures must reach 122°F (50°C).
Directly apply steam slowly and evenly to infested fabrics, items, and furniture. In most cases, bed bugs will die after being exposed to steam for a few seconds.
Be sure to let the steam penetrate seams and cracks, especially in areas with bolts and screws that bed bugs like to hide in. For large pieces of furniture like beds and upholstered couches, you may need to disassemble the parts and steam the mattresses or cushions separately.
⦿ Freezing
For certain items that are sensitive to heat, such as electronics, you can eliminate any bed bugs hiding within by effectively freezing them to death. This method is great for small valuables because it’s relatively harmless to the items, but avoid freezing any electronics with LCD screens.
Just place the items into sealed plastic bags and leave them inside a freezer with a temperature at or below 0°F (-18°C).
The items should be left in the freezer for at least 4 days to ensure that all bed bugs are killed. Bulkier items may take even longer, since the freezing temperature must reach all the way to the center of the item.
⦿ Disposal
Whether or not an item needs to be disposed of depends on the size of the infestation and whether or not you think it’s worth the time and cost to fumigate it.
Secure any infested items for disposal in garbage bags and tape the opening shut so that the bed bugs can’t escape. If the item cannot be sealed, don’t just leave it on the curb — be sure to label it as infested with bed bugs to stop anyone else from taking it home.
Professional Bed Bug Solutions
For the peace of mind that comes with knowing your bed bug infestation has been completely eliminated, consider working with a professional bed bug exterminator. Although this can be costly, depending on the size and stage of the infestation, taking this step gives you the best chance of getting rid of your bed bugs once and for all.
About Iowa Exterminator: Des Moines Iowa’s Bed Bug Experts
Iowa Exterminator is a professional pest control company based in Des Moines Iowa with years of experience helping people find, prevent, and exterminate bed bugs.
We offer effective and eco-friendly bed bug control services, using EPA-recommended Integrated Pest Management practices whenever possible to ensure safe and long-term solutions.
- With The Best Guarantee In The Business
- Discreet Services
- Customized Bed Bug Treatment & Prevention Programs
Whether it be bed bugs, roaches or general pest control. Iowa Exterminator has you covered. You, just simply give us a call and we make the pest go away. We guarantee it!!!
F.A.Q.
Answers To Your Bed Bug Questions
Bedbugs are small, reddish-brown blood-sucking, wingless insects. Bedbug bites usually clear up without treatment in a week or two. Bedbugs aren’t known to spread disease, but they can cause an allergic reaction or a severe skin reaction in some people.
Bed bugs are hard to control, but you can do it! Using insecticides alone to control bed bugs is not the best solution. Cleaning, getting rid of clutter and taking a feaw other steps are just as important as applying insecticide when you’re trying to control bed bugs.
They like to hide in small cracks and crevices close to a human environment. Bed bugs are most often found in bed parts, such as mattresses, box springs and folded areas. They can also conceal themselves behind baseboards, wallpaper, upholstery, picture frames, electrical switchplates, and in furniture crevices.
Where Do Bed Bugs Hide on Your Body? Bed bugs do not typically hide on the body. They prefer to feed, then move back to their hiding place until they are hungry again. In some cases, they may hide in your clothes or the soles of your shoes.




